Gold is now trading above $2,500 per ounce, showing signs of potentially breaking its historical highs again. Its value as a safe-haven asset shone brightly in the first weeks of August following the volatility shock experienced by the major equity markets, causing gold to rise after several downward sessions. Now that this “scare” has passed, what could continue to drive its valuation?
In the opinion of Charlotte Peuron, equity fund manager at Crédit Mutuel Asset Management, the increase in gold’s price to $2,400 per ounce has been driven by Western investors through gold ETF purchases and a more favorable financial environment for gold.
According to her outlook, given the downward trend of the dollar against other currencies and the real U.S. interest rates, the upward trend in gold is expected to continue.
“The upward trend in gold prices dates back to 2022. Three factors explain this movement: sustained demand for jewelry; investment in physical gold (coins and bars) by Asian investors; and massive purchases by central banks in emerging countries, particularly China, who wish to diversify their foreign exchange reserves and thus reduce their exposure to the U.S. dollar,” explains Peuron.
For James Luke, a commodities fund manager at Schroders, additional factors include changes in geopolitical and fiscal trends that are paving the way for sustained demand for gold, and gold miners might be poised for a significant recovery.
“Geopolitical and fiscal fragility—trends directly linked to demographic shifts and deglobalization, which, along with deglobalization, characterize the new investment paradigm that we at Schroders have dubbed the 3D Reset—combine today to forge a path toward a sustained and multifaceted global drive for gold supplies. In our view, this could trigger one of the strongest bull markets since President Nixon closed the gold window in November 1971, ending the U.S. dollar’s convertibility to gold,” he argues.
Towards a Polarized World
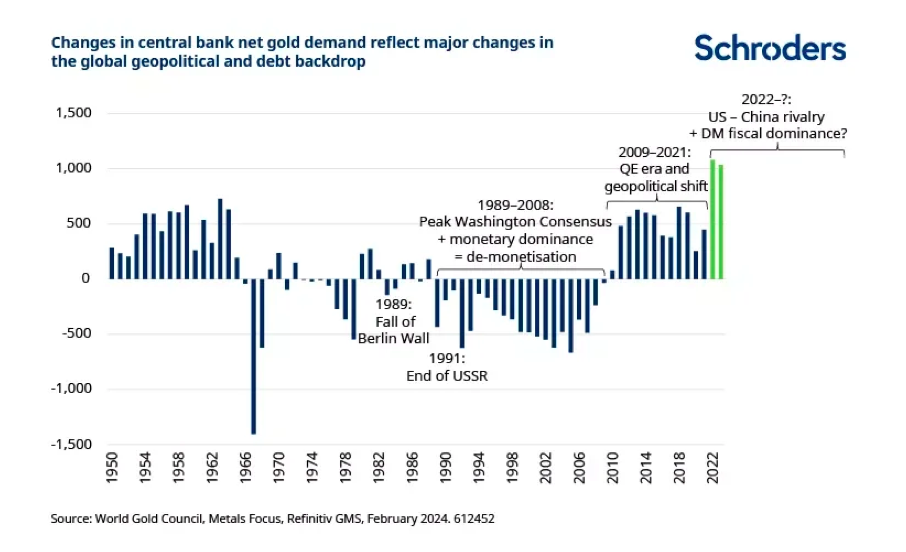
One of the most interesting reflections made by Luke is that the strength of gold reflects the shift towards a more polarized world. “The escalating tension between the United States and China, and the sanctions imposed on Russia following the invasion of Ukraine in 2022, have driven record gold purchases by central banks as a monetary reserve asset,” says the Schroders manager.
Currently, the $300 billion in frozen Russian reserve assets clearly demonstrate what the “weaponization” of the U.S. dollar—or in other words, the dollar’s hegemony—can truly mean. In his opinion, the massive issuance of U.S. Treasury bonds to finance endless deficits also raises questions about the sustainability of long-term debt. Furthermore, he notes that central banks—China, Singapore, and Poland, the largest in 2023—have been paying attention, although record purchases have only increased the share of gold in total reserves from 12.9% at the end of 2021 to 15.3% at the end of 2023.
“From a long-term perspective, central bank purchases clearly reflect the evolution of global geopolitical and monetary/fiscal dynamics. Between 1989 and 2007, Western central banks sold as much gold as they practically could, as after 1999 they were limited by gold agreements that central banks reached to maintain order in sales.
In that post-Berlin Wall and Soviet Union world, where U.S.-led liberal democracy was on the rise, globalization was accelerating, and U.S. debt indicators were quite quaint compared to today’s, the demonetization of gold as a reserve asset seemed entirely logical,” he explains.
However, he clarifies that the 2008 financial crisis, the introduction of quantitative easing, and emerging geopolitical tensions were enough to halt Western sales and quietly attract emerging market central banks to the gold market, averaging 400 tons annually between 2009 and 2021. According to Luke, “these are significant figures, less than 10% of annual demand, but not seismic.”
On the other hand, he warns that the more than 1,000 tons of gold—accounting for 20% of global demand—purchased by central banks in 2022 and 2023, a pace that continued in the first quarter of 2024, is potentially seismic. “It seems entirely plausible that the current tense dynamic between established and emerging powers, combined with the fiscal fragility looming not only over the reserve currency issued by the U.S. but over the entire developed economic bloc, could trigger a sustained move towards gold,” he argues.
In this context, and to put it bluntly, his main conclusion is that “the gold market is not large enough to absorb such a sustained move without prices rising significantly, especially if other global players also try to enter more or less at the same time.