The Fed has cut rates for the third time since March 2020 by 25 basis points, as expected. International asset managers highlight that Powell acknowledged this decision was “more difficult” than previous meetings and emphasized it was “the right decision” given current conditions. This follows the recent FOMC communication emphasizing the merits of a “gradual” normalization of policy, supported by resilient economic fundamentals and growing political uncertainty with the arrival of President Trump.
“A significant modification in the statement’s language reinforces how measured this trajectory is. The incorporation of the ‘magnitude’ and ‘timing’ signals a slower rate-cutting path, with markets now pricing in a 90% chance of a pause in January, aligning with our assessment. Powell reinforced this message, noting that while policy remains restrictive, they are ‘significantly closer to neutrality,’ justifying a more cautious approach reflected in the reduction from four to two projected cuts in 2025,” says Salman Ahmed, Global Head of Macro and Strategic Asset Allocation at Fidelity International.
For Dongyue Zhang, Head of APAC Investment Specialists for Multi-Asset Investment Solutions at abrdn, the Fed took a hawkish tone. “These signals solidify our view that the Fed will pause in January as it slows the pace of easing. We expect a cut in March, depending on continued cooling of inflation. In our view, there’s a higher risk of fewer moves, especially if we see fireworks in the early days of the Trump administration. Judging by the slight shift in the Fed’s statement, we anticipate increased volatility due to policy changes under the Trump Administration in 2025,” Zhang notes.
This new stance represents another significant adjustment in the Fed’s approach, which just three months ago led to a 50-basis-point cut. “This shift aligns with the idea that persistent inflationary pressures would prevent the Fed from implementing the easing cycle markets had anticipated. Instead, we expect the Fed to recalibrate its policy, shifting from a restrictive stance to a less restrictive one. That’s exactly what’s happening, with Powell hinting that the central bank might end consecutive cuts, potentially pausing as soon as its next meeting in January: ‘We are at, or near, a point where it will be appropriate to slow the pace of further adjustments,’” says Jean Boivin, Head of the BlackRock Investment Institute.
In this regard, George Brown, Senior U.S. Economist at Schroders, expects an additional quarter-point cut in the March 2025 meeting, followed by a 50-basis-point hike in 2026. “It’s true that the central bank’s reaction function could be distorted if its independence were undermined by the Trump Administration. However, in our view, measures to ensure that independence are sufficient to mitigate this risk, as is the fear of market backlash,” Brown explains.
The Key Lies in the Dot Plot
Regarding the Summary of Economic Projections (SEP), Ahmed notes that the Fed appeared less aggressive in the dot plot: “The 2025 dot removed two cuts, exceeding market expectations of just one less cut. This adjustment is accompanied by stronger growth projections, higher inflation, and lower unemployment in 2025,” he states. He adds: “Importantly, the committee’s assessment of the long-term neutral rate was adjusted upward, with the median rising from 2.9% to 3%, and the central trend range increasing to 2.8%-3.6%.”
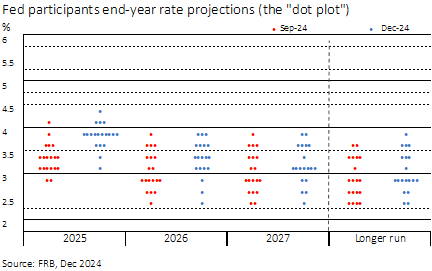
For Daniel Siluk, Head of Global Short Duration & Liquidity and Portfolio Manager at Janus Henderson, the SEP is markedly hawkish, with only two rate cuts projected for 2025, indicating heightened concern about the persistence or resurgence of inflation. “Inflation forecasts for 2025 have been revised upward to 2.5% (from 2.1%). Economic growth projections have been slightly raised for 2025, to 2.1% from 2.0%, but downgraded beyond the forecast horizon, with GDP growth for 2027 revised down to 1.9% from 2.0%. This suggests that more restrictive monetary policy has yet to make a significant dent in the economy,” notes Siluk, who observes that the market’s initial interpretation was hawkish, as evidenced by the flattening of the yield curve.
“Powell made it clear that a slower pace of cuts is the baseline case. He argued that inflation is still moving in the right direction, downplayed some of the stickiness in core inflation, and noted that the labor market is still cooling, but only gradually. We believe that if tariffs were the primary reason for the inflation uptick, we would have expected to see a softer growth forecast for 2025. Powell himself seems to have discounted tariffs, citing significant uncertainty regarding the scope, timing, and impact of tariff measures. We maintain our forecast for two more rate cuts next year, but risks have clearly shifted toward fewer (or no) cuts,” Bank of America analysts add.
David Page, Head of Macro Research at AXA IM, takes it a step further, predicting that the Fed will cut rates only once in March next year to 4.25%, depending on the magnitude of the new administration’s policies. “We are also more pessimistic about the long-term impact of these policies and expect them to weigh on growth through 2026, which we believe will prompt the Fed to resume easing in the second half of 2026. We forecast the FFR to end 2026 at 3.5%, now aligned with the Fed’s projections, but we do not believe the path will be as smooth as implied by the Fed’s mild cuts of 50, 50, and 25 basis points,” Page concludes.



