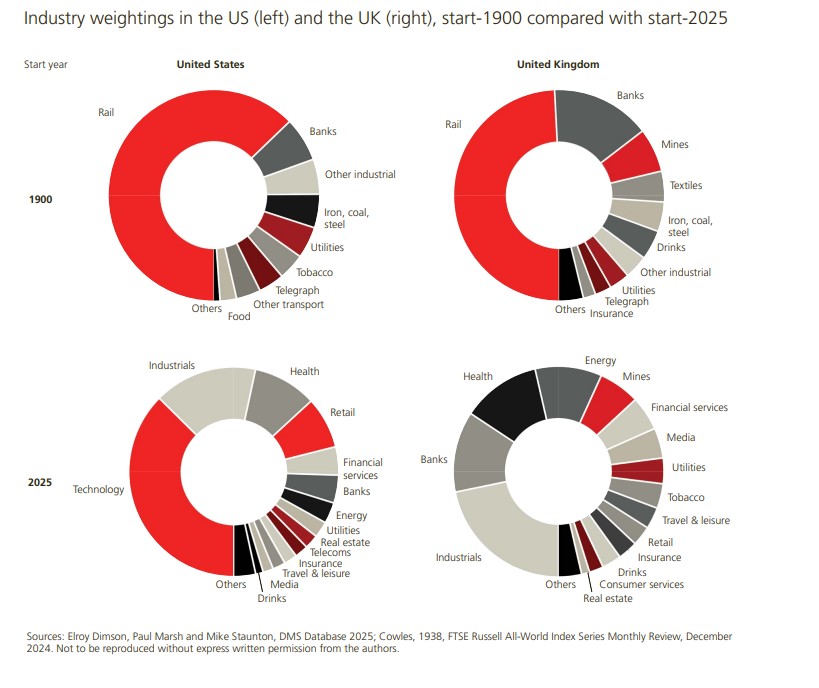
Financial markets and the industrial landscape have changed enormously since 1900, and these changes can be observed in the evolution of the composition of publicly traded companies in global markets. As depicted by UBS Global Investment in its report Global Investment Returns Yearbook, at the beginning of the 20th century, markets were dominated by railroads, which accounted for 63% of the stock market value in the U.S. and nearly 50% in the U.K.
In fact, nearly 80% of the total value of U.S. publicly traded companies in 1900 came from sectors that are now small or have even disappeared. This percentage stands at 65% in the case of the U.K. Additionally, a large proportion of companies currently listed on the stock market come from sectors that were either small or nonexistent in 1900, now representing 63% of market value in the U.S. and 44% in the U.K. “Some of the largest industries in 2025, such as energy (excluding coal), technology, and healthcare (including pharmaceuticals and biotechnology), were practically absent in 1900. Likewise, the telecommunications and media sectors, at least as we know them today, are also relatively new industries,” the report notes in its conclusions.
Among the key findings of this report, which analyzes historical data from the past 125 years, one standout conclusion is that long-term equity returns have been remarkable. According to the document, equities have outperformed bonds, Treasury bills, and inflation in all countries. An initial investment of 1 dollar in U.S. stocks in 1900 had grown to 107,409 dollars in nominal terms by the end of 2024.
Concentration, Synchronization, and Inflation: Three Clear Warnings
Throughout this historical evolution, the report’s authors have identified concentration as a growing concern. “Although the global equity market was relatively balanced in 1900, the United States now accounts for 64% of global market capitalization, largely due to the superior performance of major technology stocks. The concentration of the U.S. market is at its highest level in the past 92 years,” they warn.
In contrast, diversification has clearly helped manage this concentration and, more importantly, volatility. According to the report’s conclusions, while globalization has increased the degree of market synchronization, the potential benefits of international diversification in reducing risks remain significant. For investors in developed markets, emerging markets continue to offer better diversification prospects than other developed markets.
Finally, the conclusions emphasize that inflation is a key factor to consider in long-term returns. In this regard, the authors’ analysis shows that asset returns have been lower during periods of rising interest rates and higher during cycles of monetary easing. “Similarly, real returns have also been lower during periods of high inflation and higher during periods of low inflation. Gold and commodities stand out among the few effective hedges against inflation. Since 1972, gold price fluctuations have shown a positive correlation of 0.34 with inflation,” the report states.
Key Insights from the Report’s Authors
Following the release of this report, Dan Dowd, Head of Global Research at UBS Investment Bank, commented: “I am pleased to once again collaborate with professors Dimson, Marsh, and Staunton, as well as our colleagues from Global Wealth Management, in presenting the 2025 edition of the Global Investment Returns Yearbook. The 2025 edition marks an important milestone. With 125 years of data, it provides our clients across the firm with a valuable framework for addressing contemporary challenges through the lens of financial history.”
Meanwhile, Mark Haefele, Chief Investment Officer of UBS Global Wealth Management, highlights that the Global Investment Returns Yearbook can help us understand the long-term impacts of following principles such as diversification, asset allocation, and the relationship between return and risk. “Once again, it teaches us that having a long-term perspective is crucial and that we should not underestimate the value of a disciplined investment approach,” Haefele states.
Finally, Professor Paul Marsh of the London Business School notes that “equity returns in the 21st century have been lower than in the 20th century, while fixed income returns have been higher. However, equities continue to outperform inflation, fixed income, and cash. The global stock market has delivered an annualized real return of 3.5% and a 4.3% premium over cash. The ‘law’ of risk and return remains valid in the 21st century.”
Financial markets and the industrial landscape have changed enormously since 1900, and these changes can be observed in the evolution of the composition of publicly traded companies in global markets. As depicted by UBS Global Investment in its report Global Investment Returns Yearbook, at the beginning of the 20th century, markets were dominated by railroads, which accounted for 63% of the stock market value in the U.S. and nearly 50% in the U.K.
In fact, nearly 80% of the total value of U.S. publicly traded companies in 1900 came from sectors that are now small or have even disappeared. This percentage stands at 65% in the case of the U.K. Additionally, a large proportion of companies currently listed on the stock market come from sectors that were either small or nonexistent in 1900, now representing 63% of market value in the U.S. and 44% in the U.K. “Some of the largest industries in 2025, such as energy (excluding coal), technology, and healthcare (including pharmaceuticals and biotechnology), were practically absent in 1900. Likewise, the telecommunications and media sectors, at least as we know them today, are also relatively new industries,” the report notes in its conclusions.

Among the key findings of this report, which analyzes historical data from the past 125 years, one standout conclusion is that long-term equity returns have been remarkable. According to the document, equities have outperformed bonds, Treasury bills, and inflation in all countries. An initial investment of 1 dollar in U.S. stocks in 1900 had grown to 107,409 dollars in nominal terms by the end of 2024.
Concentration, Synchronization, and Inflation: Three Clear Warnings
Throughout this historical evolution, the report’s authors have identified concentration as a growing concern. “Although the global equity market was relatively balanced in 1900, the United States now accounts for 64% of global market capitalization, largely due to the superior performance of major technology stocks. The concentration of the U.S. market is at its highest level in the past 92 years,” they warn.
In contrast, diversification has clearly helped manage this concentration and, more importantly, volatility. According to the report’s conclusions, while globalization has increased the degree of market synchronization, the potential benefits of international diversification in reducing risks remain significant. For investors in developed markets, emerging markets continue to offer better diversification prospects than other developed markets.
Finally, the conclusions emphasize that inflation is a key factor to consider in long-term returns. In this regard, the authors’ analysis shows that asset returns have been lower during periods of rising interest rates and higher during cycles of monetary easing. “Similarly, real returns have also been lower during periods of high inflation and higher during periods of low inflation. Gold and commodities stand out among the few effective hedges against inflation. Since 1972, gold price fluctuations have shown a positive correlation of 0.34 with inflation,” the report states.
Key Insights from the Report’s Authors
Following the release of this report, Dan Dowd, Head of Global Research at UBS Investment Bank, commented: “I am pleased to once again collaborate with professors Dimson, Marsh, and Staunton, as well as our colleagues from Global Wealth Management, in presenting the 2025 edition of the Global Investment Returns Yearbook. The 2025 edition marks an important milestone. With 125 years of data, it provides our clients across the firm with a valuable framework for addressing contemporary challenges through the lens of financial history.”
Meanwhile, Mark Haefele, Chief Investment Officer of UBS Global Wealth Management, highlights that the Global Investment Returns Yearbook can help us understand the long-term impacts of following principles such as diversification, asset allocation, and the relationship between return and risk. “Once again, it teaches us that having a long-term perspective is crucial and that we should not underestimate the value of a disciplined investment approach,” Haefele states.
Finally, Professor Paul Marsh of the London Business School notes that “equity returns in the 21st century have been lower than in the 20th century, while fixed income returns have been higher. However, equities continue to outperform inflation, fixed income, and cash. The global stock market has delivered an annualized real return of 3.5% and a 4.3% premium over cash. The ‘law’ of risk and return remains valid in the 21st century.”




